Keywords: Red Light Therapy Wavelengths, RLT Safety, Photobiomodulation (PBM) Contraindications, Optimal Wavelengths, LED Light Therapy Risks.
Red Light Therapy (RLT), also clinically termed Photobiomodulation (PBM) or Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), has transitioned from niche clinical treatment to mainstream wellness. Its efficacy is rooted in the precise use of red and near-infrared (NIR) light to stimulate cellular function. This guide provides a professional overview of the optimal wavelengths, the mechanisms of action, and critical safety guidelines to ensure maximum benefit with minimal risk.

I. The Scientific Core: Wavelengths and Mechanism of Action
The power of RLT lies in its ability to non-invasively interact with the body's cellular machinery.
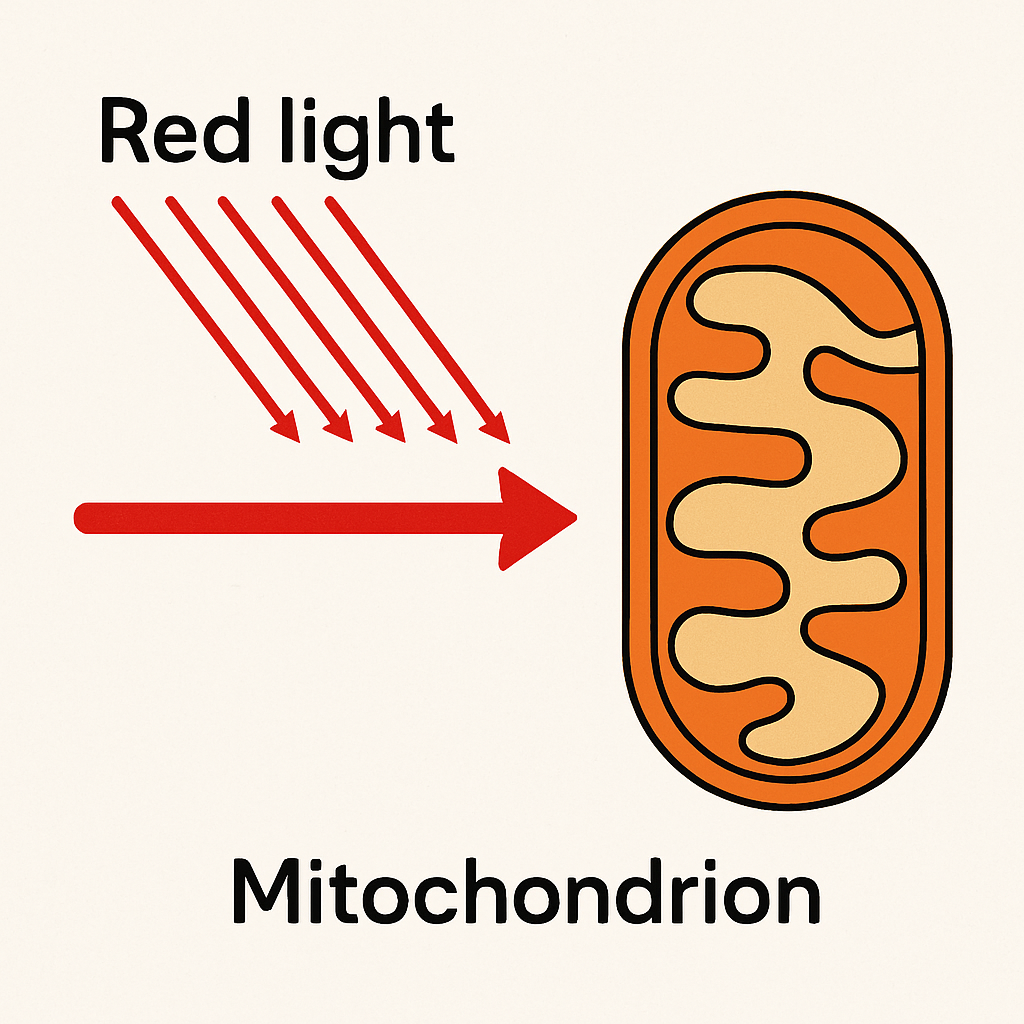
A. The Mitochondria-Light Connection
PBM works by targeting the mitochondria, the cell's "powerhouses." Specific light wavelengths are absorbed by Cytochrome C Oxidase (CCO) within the mitochondrial membrane.
-
Mechanism: Light absorption enhances the efficiency of the electron transport chain, significantly boosting Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) production. This ATP surge provides the necessary energy for accelerated cellular repair and regeneration.
-
Molecular Signaling: This process also facilitates the transient release of Nitric Oxide (NO), a potent vasodilator. NO release improves local microcirculation and oxygen delivery, playing a critical role in reducing oxidative stress and modulating inflammation.
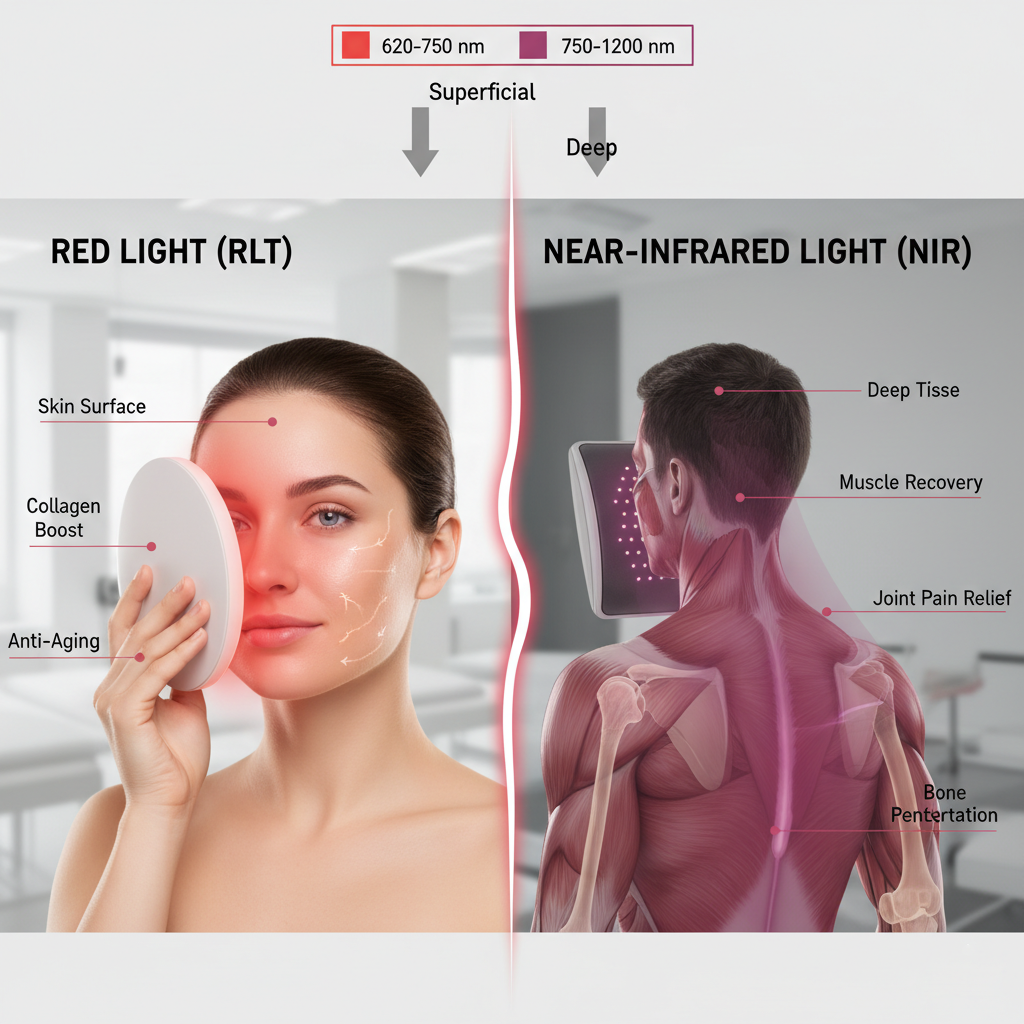
B. Wavelength Dosimetry: Depth and Target Tissue
The therapeutic outcome is directly dependent on the light's wavelength, which dictates its depth of penetration into the tissue—a core concept known as Dosimetry.
| Wavelength Range | Light Type | Primary Penetration Depth | Key Therapeutic Targets |
| 630 nm – 700 nm | Red Light | Superficial (Epidermis/Dermis, up to 10 mm) | Skin Health, Collagen Production, Superficial Wound Healing, Anti-aging (e.g., 660 nm is commonly studied for skin). |
| 810 nm – 880 nm | Near-Infrared (NIR) | Deep (Muscle, Joint, Nerve, up to 50 mm) | Pain Management, Muscle Recovery, Joint Inflammation, Neurological Support (e.g., 850 nm is widely used for deep tissue). |
II. RLT Benefits: Evidence-Based Applications
PBM's versatility allows for application across multiple health domains:
-
Dermatology and Aesthetics: RLT stimulates fibroblast activity to enhance collagen and elastin synthesis, visibly reducing fine lines, improving skin texture, and aiding in the resolution of acne and scars.
-
Musculoskeletal Recovery: High-powered NIR light is clinically used to accelerate post-exercise recovery, reduce Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS), and alleviate chronic pain conditions like osteoarthritis by penetrating deep into joints and muscles.
-
Wound Healing and Tissue Repair: The ability of RLT to accelerate wound healing and tissue repair is a key benefit. By enhancing cellular regeneration and blood flow (via NO release), it may speed up the recovery of injuries and surgical wounds, reducing downtime and improving overall healing outcomes.
-
Mood Enhancement and Mental Health Benefits: Emerging research suggests RLT might play a role in mood enhancement. It is thought to influence the release of neurotransmitters and modulate circadian rhythms, potentially improving mood and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
III. Contraindications for Red Light Therapy: Critical Safety Considerations
While RLT is generally regarded as safe, its non-invasive nature does not eliminate the need for strict adherence to safety guidelines and the consideration of contraindications. Professional consultation is essential before beginning RLT, especially if you have underlying health conditions.

A. Pregnancy and Uncertain Effects
-
Guidance: The effects of red light therapy on pregnant individuals remain under-researched. As a precautionary measure, it is generally advised to avoid red light therapy during pregnancy unless explicitly approved by a healthcare provider. Safety data is limited, and potential risks outweigh unproven benefits.
B. Photosensitive Disorders and Precautionary Measures
-
Risk: Individuals with photosensitive disorders, such as lupus or porphyria, should exercise caution. These conditions can make the skin more sensitive to light, potentially exacerbating symptoms.
-
Medication Risk: The use of photosensitizing drugs (e.g., certain antibiotics, St. John's Wort) must also be considered, as they can induce severe light sensitivity.
-
Action: Consulting with a healthcare provider (e.g., a Dermatologist) is essential to evaluate the risks and benefits.
C. Cancer Considerations and Professional Guidance
-
Complexity: The relationship between red light therapy and cancer is complex. While some research suggests potential therapeutic benefits in specific settings, there is significant concern about the possibility of stimulating cancerous growths due to RLT's cell-proliferation-enhancing properties.
-
Action: Individuals with a history of cancer or those with active neoplastic lesions should seek professional medical advice before pursuing red light therapy. Do not apply RLT over an area with known active cancer.
IV. RLT Side Effects and Safety Protocols
To minimize risks and ensure a positive experience, adhering to safety measures is crucial.
A. Potential Side Effects
-
Temporary Redness and Skin Tightness: One of the most commonly reported side effects is temporary redness or a feeling of tightness in the skin following a session. This reaction is typically mild and subsides quickly, often requiring no intervention.
-
Dry Skin and Hydration Strategies: Extended use of red light therapy may lead to dryness in the treated areas. To combat this, it's recommended to apply a moisturizer post-session to maintain skin hydration.
B. Essential Safety Measures
-
Eye Safety Concerns: Direct exposure to red light, especially from high-intensity devices, can pose a risk to the eyes. It is crucial to wear protective eyewear during treatment to prevent potential damage.
-
Choosing Certified and Reputable Devices: When selecting a device, prioritize those that are FDA-approved or certified by reputable organizations. This ensures that the device meets safety and efficacy standards, minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
-
Adhering to Recommended Usage Guidelines: Following the manufacturer's guidelines regarding session duration and frequency is essential. Overuse or incorrect application can lead to adverse effects, such as skin irritation or burns.
-
Possible Hazards (Skin Burns): Improper use of high-intensity devices or excessive exposure can result in skin burns. To prevent this, always follow the device's instructions carefully and limit exposure time as recommended.
Conclusion: Red light therapy holds promise for numerous potential benefits, but understanding the risks and taking necessary precautions is essential for a safe and effective experience. By being informed about the specific side effects, contraindications, and safety measures, you can maximize the therapeutic potential of this innovative treatment while minimizing any possible hazards. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns or underlying health conditions before starting red light therapy.